OSTEOPATHY
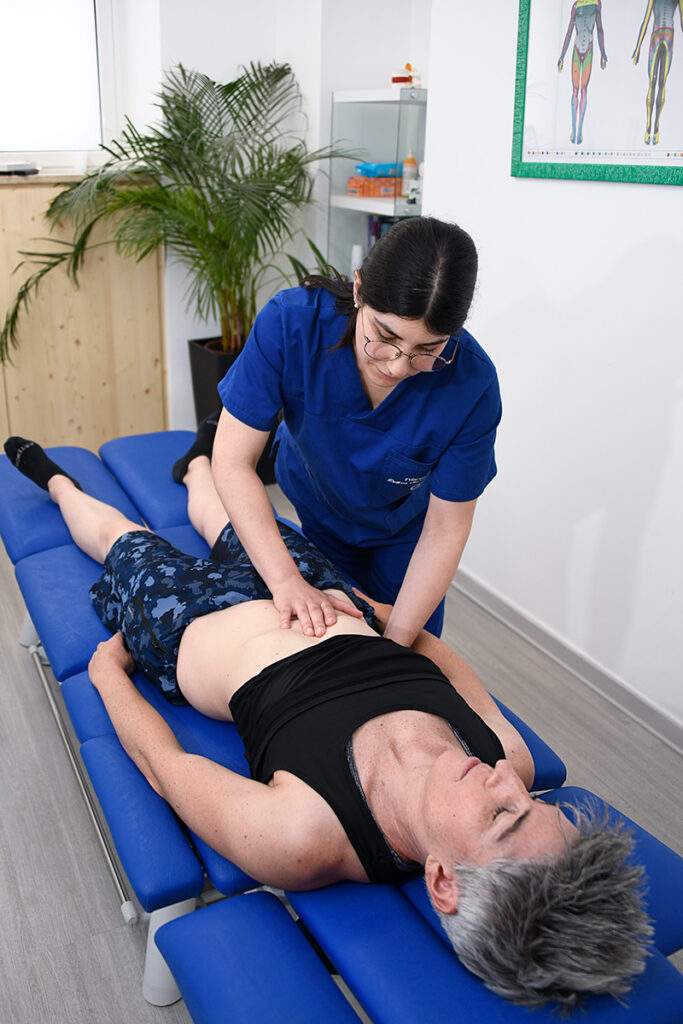
Osteopathy, or osteopathic medicine, is a form of alternative medicine that embraces the concept of the unity of structure and function of the body in health and disease. The osteopathic profession consists of various preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic measures designed to maintain or restore structural integrity and consequently ensure its physiological function.
Osteopathic treatment consists of a series of manual techniques and does not involve the use of machinery. Each treatment is unique and personalized for the individual patient and may include various techniques such as:
- Articular techniques
- Muscle energy techniques
- High-velocity low-amplitude (thrust) techniques
- Soft tissue techniques
- Functional techniques
- Craniosacral techniques
- Visceral manipulation
The goals of osteopathic treatment include pain reduction, increased mobility, decreased body tensions, improved musculoskeletal function, disease prevention, and restoration of the body’s overall balance.
Physiotherapy or osteopathy?
Physiotherapy and osteopathy are both medical disciplines that aim to improve patient health and well-being, but they have slightly different approaches and methodologies.
Physiotherapy is a paramedical discipline that focuses on rehabilitation and improving physical function through therapeutic exercise, manual therapy, electrotherapy, and other modalities.
Osteopathy is a form of alternative medicine based on the philosophy that the body is capable of self-healing and that well-being depends on the balance between body structure (bones, muscles, connective tissues) and its function.
In summary, while physiotherapy primarily focuses on rehabilitation and physical therapy through a range of methods and modalities, osteopathy places greater emphasis on the structural and functional balance of the body, mainly using manual therapy to promote natural healing. Both disciplines can be complementary and used together to achieve optimal results in patient care.
