IONTOPHORESIS, TENS, ELECTRICAL STIMULATION, ULTRASOUND
IONTOPHORESIS
Iontophoresis is a technique that uses continuous electric energy therapeutically to insert and deliver drugs through the skin directly into the area of interest, without affecting other non-targeted organs, thus limiting potential side effects or damage to the stomach, liver, and kidneys. This system allows for easy penetration of any medicinal solution through the skin, and depending on the chosen drug, it can have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, muscle relaxant, recalcifying, or sclerosing action. It is not recommended for patients with pacemakers, pregnant women, peri-cardiac stimulation, ulcers, or any confirmed allergic reaction to the current.TENS
TENS is the acronym for “Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation,” a non-invasive therapy that uses small electrical currents to relieve pain. The main objectives of TENS are:- Pain Reduction: TENS is commonly used to reduce acute and chronic pain in various conditions, such as muscle pain, joint pain, back pain, diabetic neuropathy, arthritis pain, trauma or post-operative pain, and more.
- Modulation of Pain Perception
- Reduction of Inflammation: In some cases, TENS can also help reduce local inflammation, providing additional pain relief.
- Improvement of Circulation: The electrical currents used in TENS can also improve blood circulation in the treated area, helping to reduce edema and promote muscle recovery.
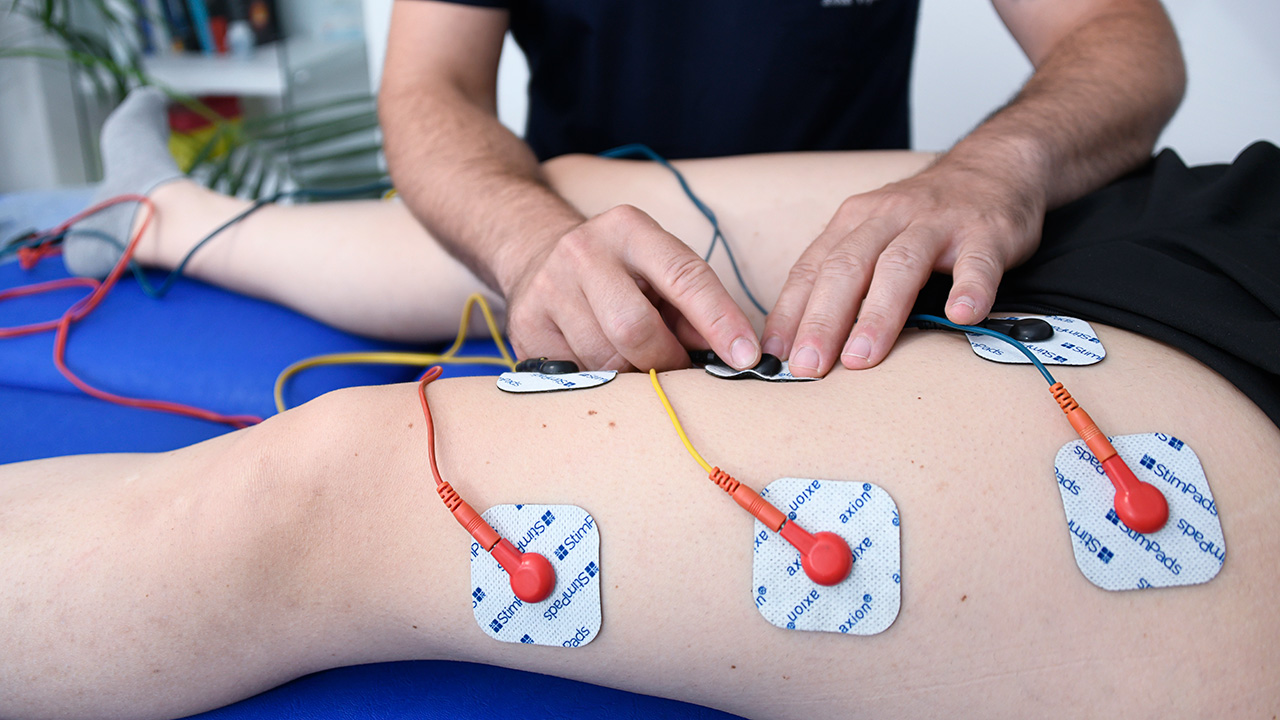
ELECTRICAL STIMULATION
Electrical stimulation, or electrotherapy stimulation, is a therapeutic technique that uses electrical current pulses to provoke muscle contractions. This approach is employed for various purposes, including muscle rehabilitation, enhancement of athletic performance, and pain relief.Principle of Operation
The fundamental principle of electrical stimulation is the application of electrical impulses to specific muscle groups. Electrodes, placed on the skin, transmit these impulses, which mimic the natural signals sent from the central nervous system to the muscles. This causes a muscle contraction similar to what occurs during regular physical exercise.Types of Electrical Stimulation
There are several types of electrical stimulation, each with specific therapeutic applications:- Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (EMS): Primarily used for muscle strengthening, rehabilitation, and the prevention of muscle atrophy. EMS is particularly beneficial for patients who cannot perform traditional exercises due to injuries or disabilities.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): Mainly used for pain relief. The electrical impulses block pain transmission to the brain and stimulate the production of endorphins, which act as natural painkillers.
- Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES): Used to improve motor functions in patients with neurological damage, such as that caused by strokes or spinal cord injuries. FES helps restore functional movements by stimulating paralyzed muscles.
Clinical Applications
Electrical stimulation has a wide range of clinical applications. In physiotherapy, it is used to rehabilitate weakened or atrophied muscles, often following surgeries or trauma. Electrical stimulation can accelerate recovery, improve muscle strength, and prevent further injuries. In sports, electrical stimulation is used to enhance athletic performance. Athletes can benefit from faster recovery, increased muscle strength, and endurance. This type of therapy is also used for muscle warm-up before competitions or intensive training sessions. For patients with chronic pain, TENS offers a non-pharmacological alternative for pain management. It is particularly useful for conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and chronic lower back pain.Electrical stimulation, or electrotherapy stimulation, is a therapeutic technique that uses electrical current pulses to provoke muscle contractions. This approach is employed for various purposes, including muscle rehabilitation, enhancement of athletic performance, and pain relief.ULTRASOUND
Ultrasound therapy devices consist of a head, usually metallic, connected to a transducer. The transducer is a device that converts electrical current into a vibration.
When the transducer is powered with a suitably generated current, it produces an ultrasonic frequency vibration that, through the head, can be used to treat selected areas of the body. The ultrasonic vibration has a frequency of one million cycles per second and can achieve a therapeutic effect up to 3-4 centimeters deep.
The main clinical applications of ultrasound that have been reported to have clinical value include:
- Pain reduction
- Treatment of contractures in collagen tissue (scar tissue) and connective tissues
- Arthritis, bursitis
